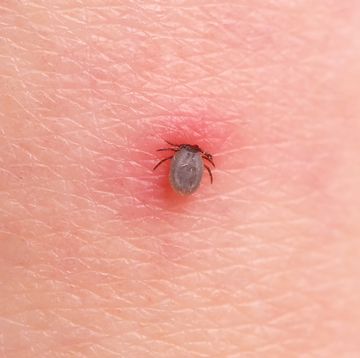
10 Types of Ticks That Transmit Diseases, Where They Live, and How to Identify Them
From the east coast to the mountains to the Pacific shores, here are the tick species that can make you sick.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Why Trust Us?
It’s easy to assume that a tick is a tick, but there are actually different species of ticks out there. And, unfortunately, there is a range of diseases they can transmit. That’s why it’s so crucial to at least have some idea of how to spot the different types of ticks that live in your area.
“Different types of ticks transmit different types of germs,” says Thomas Mather, Ph.D., director of the University of Rhode Island’s Center for Vector-Borne Disease. And, while Lyme disease is the big one many people automatically associate with ticks, there are plenty of other tick-borne diseases to have on your radar as well. “You want to be able to identify what that tick is so that, if you were to get bitten and become sick, you’d have an idea of where to start,” says Ian Williams, technical services manager at Orkin.
That’s why it’s a good idea to hold onto the tick, if you can, says Cynthia Lord, Ph.D., an entomologist and researcher at UF/IFAS Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory. “If a tick is attached, saving the tick can provide additional information to your doctor should you have symptoms,” she says.
How to identify different types of ticks
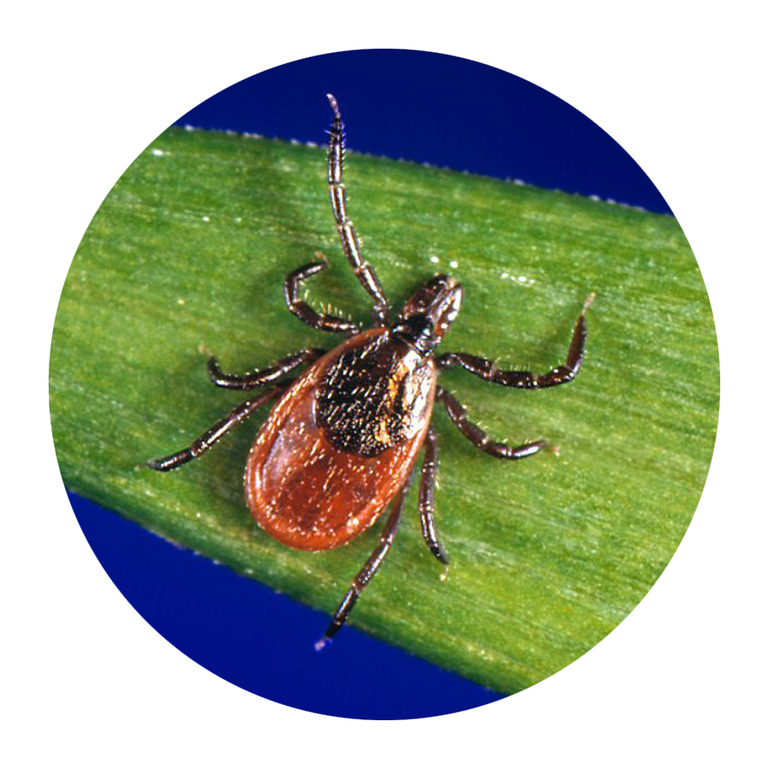
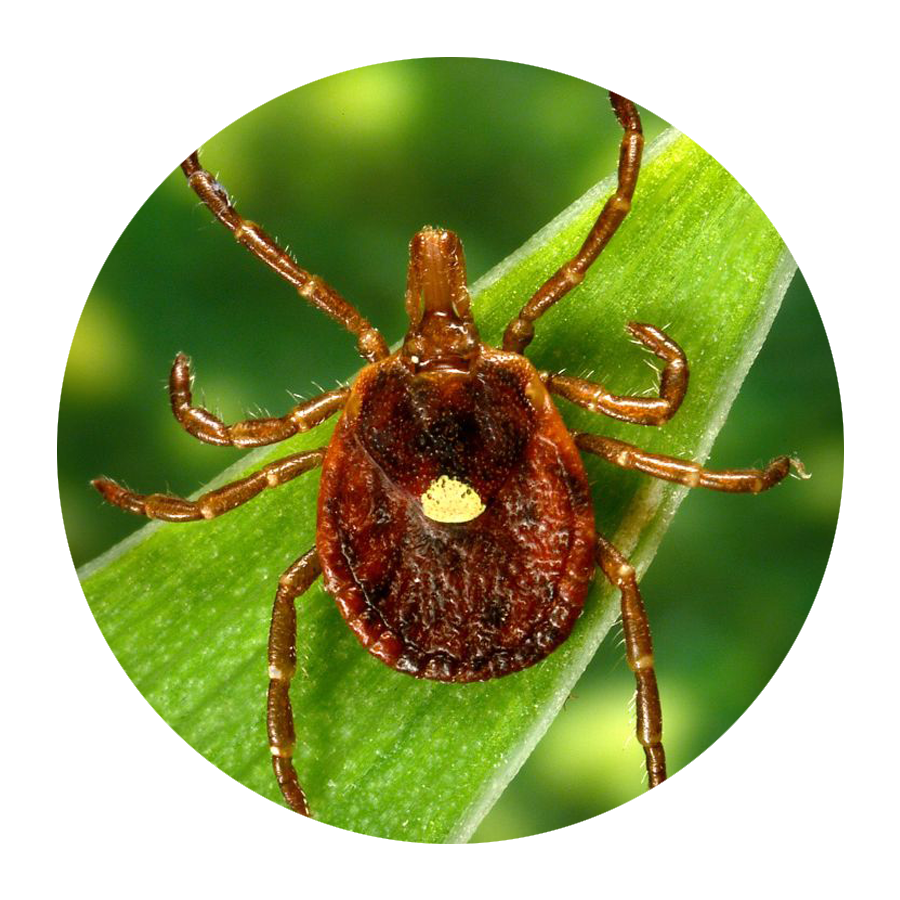
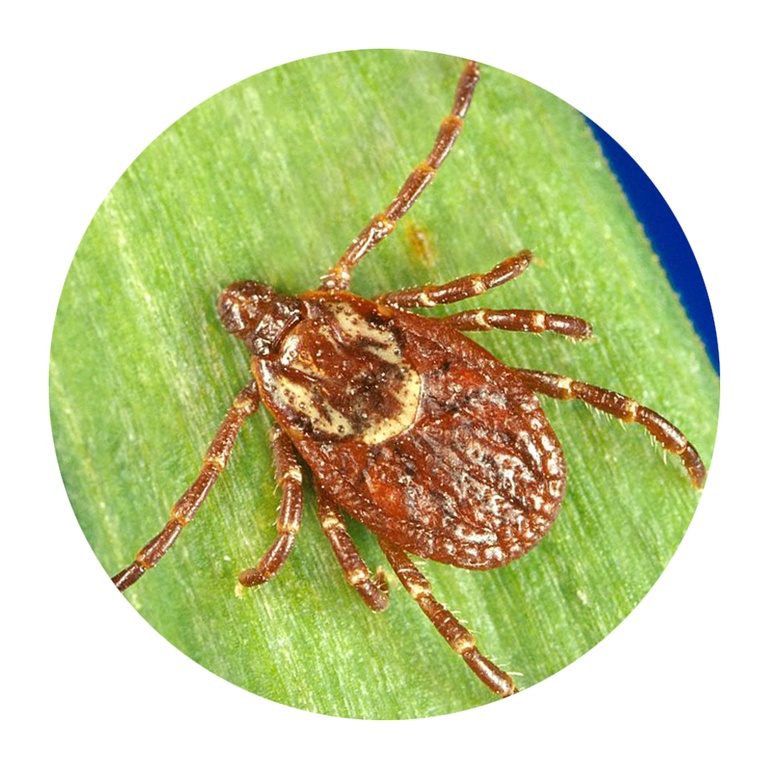
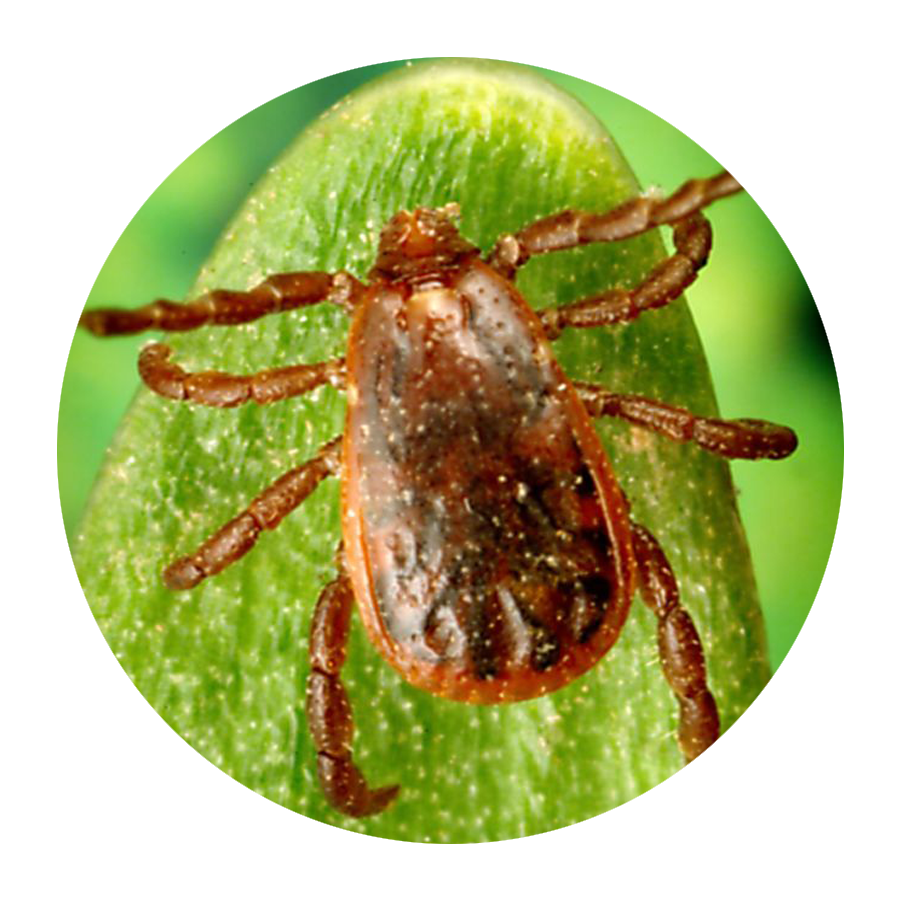
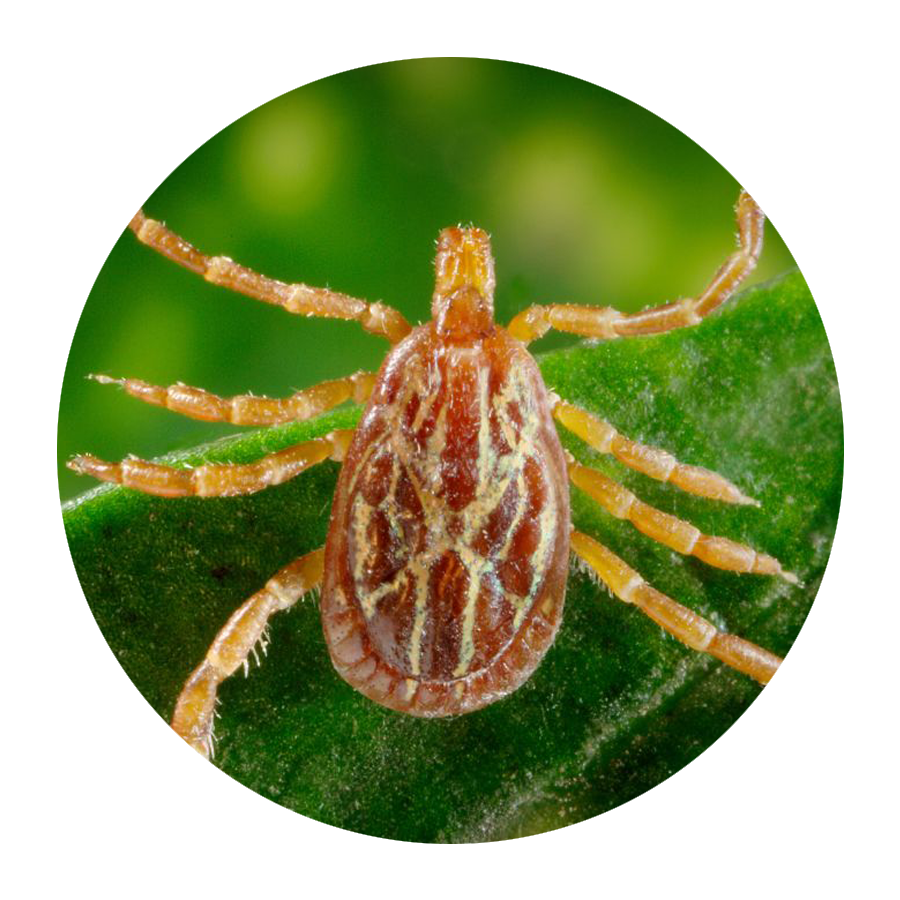
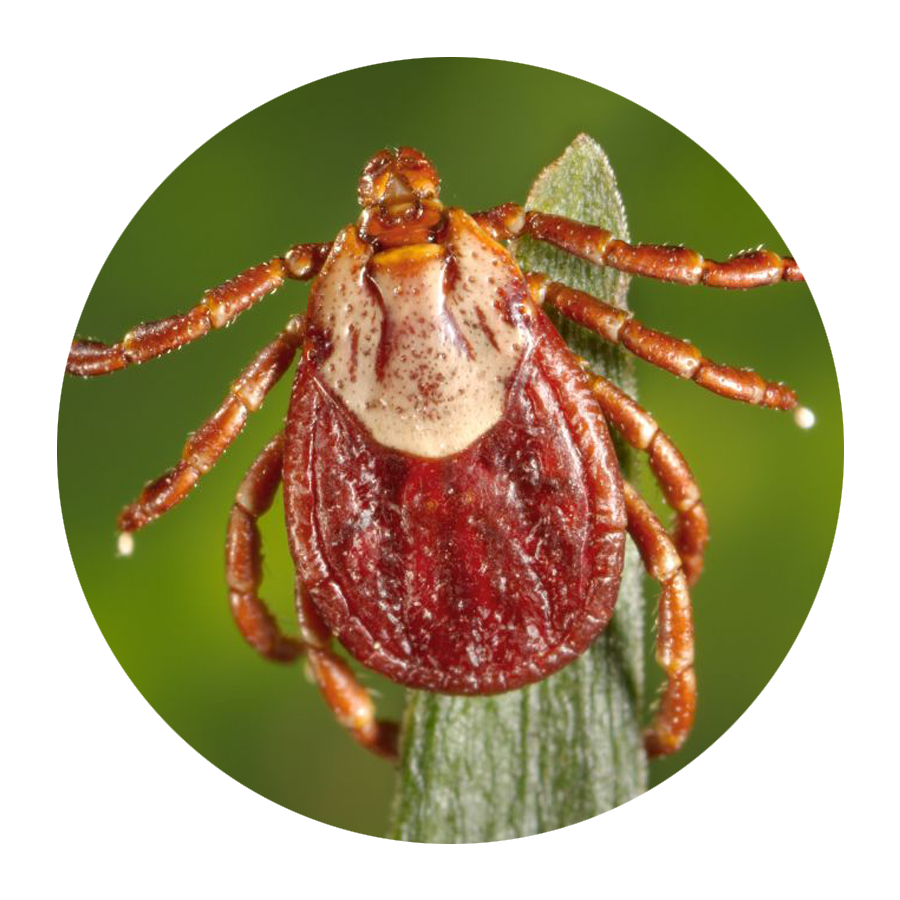
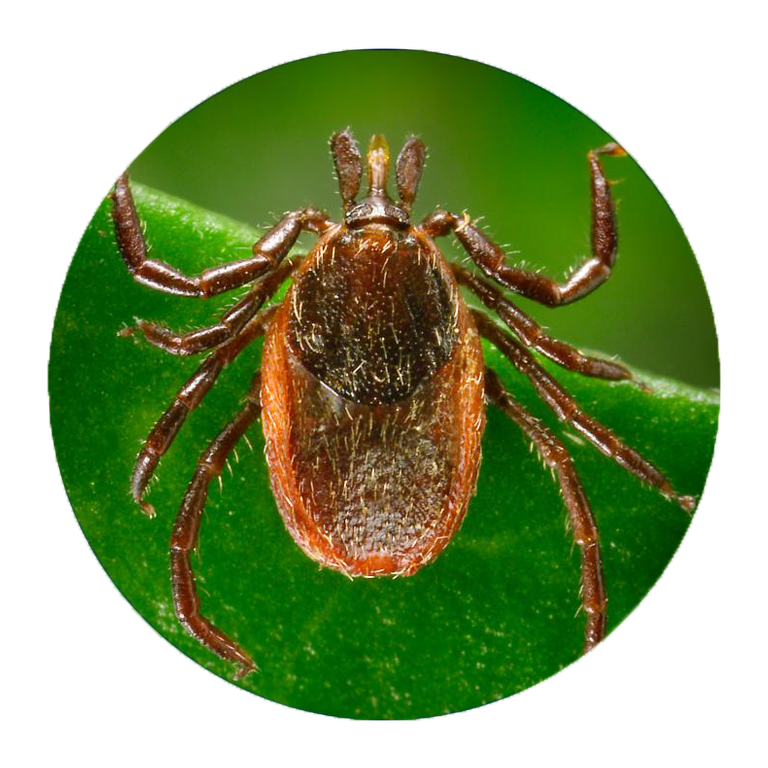
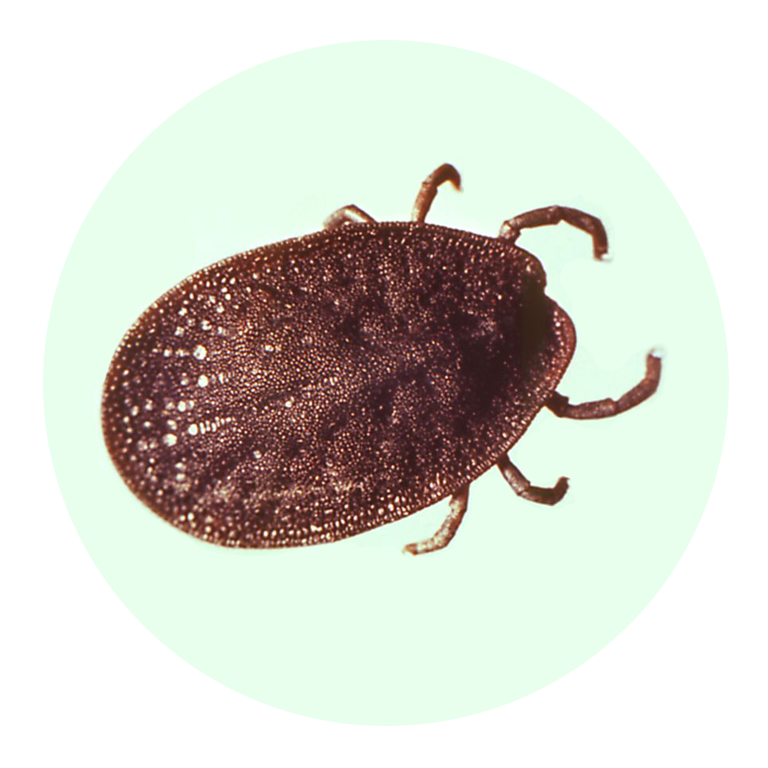
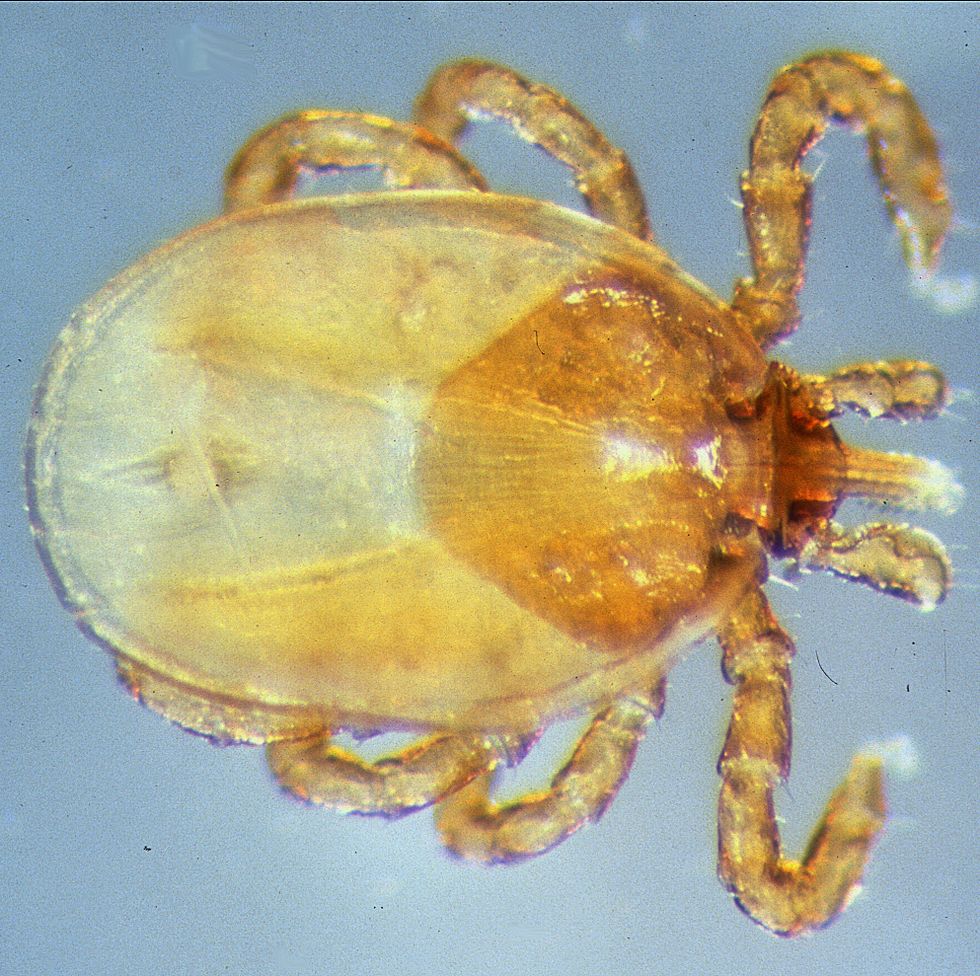
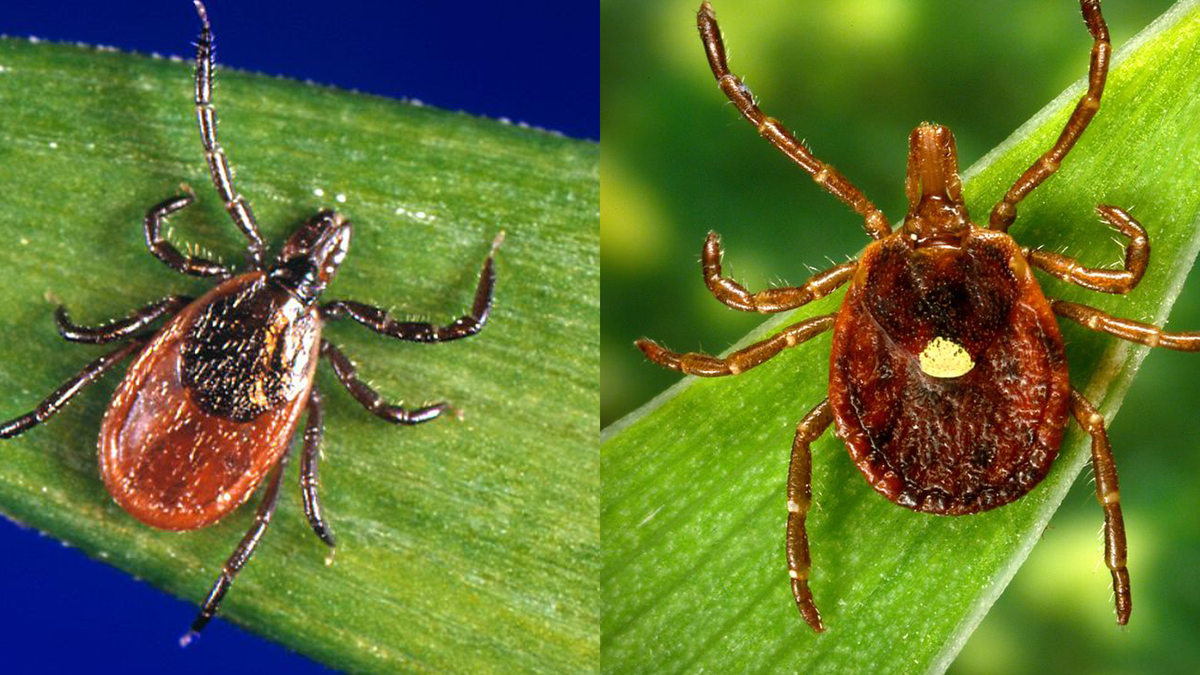
If you’re not an entomologist, it can be tricky to identify a tick species. Still, Mather says there are certain features that are unique to each type of tick that can help you sort them out.
According to LymeDisease.org, there are two families of ticks found in the United States: Ixodidae (hard ticks) and Argasidae (soft ticks). Of the 700 species of hard ticks and 200 species of soft ticks found throughout the world, only a few are known to bite and transmit disease to humans.
Keep in mind, though, that other small insects can be confused for ticks. In general, ticks only have two body segments—a fused head and abdomen, Williams says. Larval ticks (i.e. baby ticks) will have six legs, but nymphal and adult ticks will have eight legs. “Ticks have no antennae or wings,” Williams adds.
“Ticks are not insects,” Lord points out. “They are in the same class as spiders and scorpions.” And, she adds, their “body shape and movement are different than most insects or spiders.”
Types of ticks
Think you’ve spotted a tick on your body? These are the different types of ticks out there and the diseases they can transmit, just in case you start feeling off after your latest outdoor adventure.

Jessica Migala is a health writer specializing in general wellness, fitness, nutrition, and skincare, with work published in Women’s Health, Glamour, Health, Men’s Health, and more. She is based in the Chicago suburbs and is a mom to two little boys and rambunctious rescue pup.
Madeleine, Prevention’s assistant editor, has a history with health writing from her experience as an editorial assistant at WebMD, and from her personal research at university. She graduated from the University of Michigan with a degree in biopsychology, cognition, and neuroscience—and she helps strategize for success across Prevention’s social media platforms.

The Best Tick Repellents to Prevent Bites
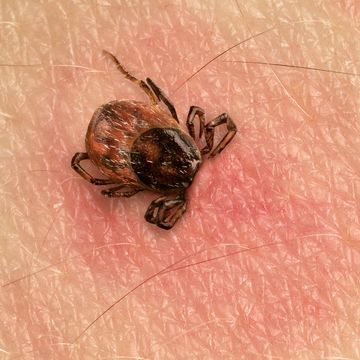
These Pictures Can Help You Identify a Tick Bite

What Is Alpha-Gal Syndrome?

How to Prevent Tick Bites in the First Place